Table Of Content

On the other hand, it has been shown that the downward growth of early anagen follicle occurs by growth pressure.25,26 It has to work against the compressive force described above. As the cushion reduces, the hair follicle needs to strive against a higher pressure to reach its terminal follicle size. This is a local demand, and there is a mechanism for increasing the effect of androgens locally without raising systemic androgen levels. 5-alpha reductase enzyme activity increases at the locale and converts more testosterone to DHT, which has severalfold greater affinity for androgen receptors than testosterone.
Can diabetes lead to hair loss? - The Indian Express
Can diabetes lead to hair loss?.
Posted: Wed, 29 Nov 2023 08:00:00 GMT [source]
How to reduce DHT levels
As an adult, your body converts about 10% of your testosterone (the main androgen) into DHT each day. This takes place in the genital skin and prostate in people AMAB and in the skin in people AFAB. It also happens in other parts of your body, such as your liver. Having high levels of testosterone does not necessarily cause hair loss. This is essentially a part of the telogen stage and is when hair is shed from the follicle.
Finally a cure for baldness? Scientists regrow hair using stem cells - Earth.com
Finally a cure for baldness? Scientists regrow hair using stem cells.
Posted: Tue, 06 Jun 2023 07:00:00 GMT [source]
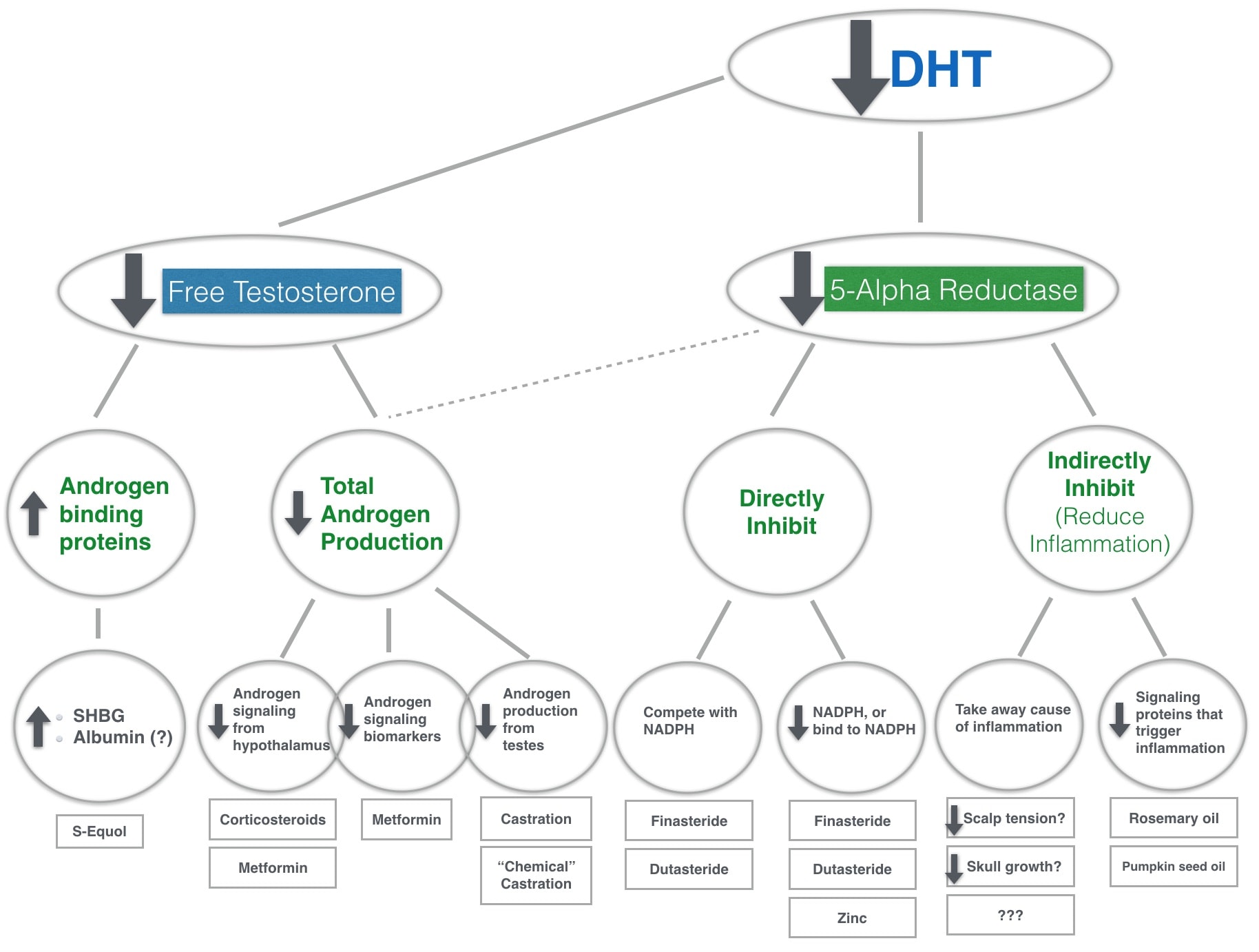
How Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) Causes Hair Loss
It’s commonly used for cooking thanks to its ability to withstand high cooking temperatures. The oil also has various applications in beauty, skin care, hair care, and overall health. Pubic hair and underarm hair growth seem to be stimulated by testosterone rather than DHT.
Best DHT Blocking Shampoo: 3 Options
High levels of DHT are usually a result of excess testosterone production. It’s estimated that about two-thirds of American men will experience some degree of appreciable hair loss by their mid-30s, and this number rises to to about 85 percent by the time a man reaches his 50s. It’s worth noting that although consuming soy is commonly thought to decrease testosterone levels in men, most available evidence suggests that this does not apply if it’s consumed in moderation. As such, additional trials in humans are necessary before pumpkin seed oil can be recommended for fighting hair loss. Preclinical studies have demonstrated that curcumin lowers DHT levels by blocking the action of the alpha-5 reductase enzyme. While these types of studies — known as preclinical studies — help researchers identify whether a specific treatment may be effective or safe, their results can’t be translated to humans.
Does Vitamin E Help Hair Growth?
Celiac disease is an autoimmune condition that causes digestive dysfunction in response to eating gluten, a protein commonly found in foods like bread, oats, and other grains. DHT isn’t the only reason you may be seeing your hair thinning or falling out. Pumpkin seed oil is another DHT blocker that’s been shown to be successful. The size and shape of your head may also contribute to how quickly DHT shrinks your follicles. Prevention is better than cure so if you notice signs of thinning, speak to a doctor, trichologist or a professional hairdresser. Rest assured that this trying time can end, and your beautiful locks will once again be on your head instead of in the brush or shower drain.
Your hair growth serum questions, answered
During puberty, children who are genetically male with 5-alpha reductase deficiency experience a lack of facial hair growth. Because their body still makes testosterone, they still experience voice deepening, muscle mass increase and penis enlargement. Androgenic alopecia is commonly known as male pattern hair loss. The hair loss usually happens on the top and frontal regions of your scalp, causing your hairline to recede over time.
One of its symptoms can be an increase in male hormones, including DHT, which can contribute to hair thinning or loss in women. This hormone has a key role in puberty, developing features typically linked with males, like body hair, a deeper voice and muscle mass. After puberty, DHT continues to influence things like hair thinning, fat distribution and even your mood. Technically, DHT blockers are any chemicals that prevent DHT from binding to the receptors in your hair follicles.
Testosterone can bind and active the androgen receptor on hair follicles. However, DHT can bind and activate the receptor with five times greater affinity, which is why high DHT levels can lead to hair loss. Being gentle with your hair while it’s experiencing change is important so as not to exacerbate any thinning. It goes without saying that excessive heat and chemical treatments aren’t a good idea, but try and opt for protective hairstyles too.
Stress
It can also shift follicles into the telogen phase, a resting phase that can see hair fall out more easily. Most baldness is caused by genetics (male-pattern baldness and female-pattern baldness). See your doctor if you are distressed by persistent hair loss in you or your child and want to pursue treatment. For women who are experiencing a receding hairline (frontal fibrosing alopecia), talk with your doctor about early treatment to avoid significant permanent baldness. Spironolactone is an antiandrogen that is used to treat DHT-related hair loss in women that does not respond to standard treatments such as minoxidil.
Keep on reading to find out more on the effects of DHT and its involvement in hair loss/growth, and the best ways to manage its repercussions in hair health. The foods we consume play a role in maintaining healthy DHT levels. A balanced diet that includes foods like spinach, kale, pumpkin seeds, mushrooms, dark chocolate, walnuts, and almonds can help regulate the production of DHT. Reducing the consumption of red meat, dairy, eggs, and wheat may also be beneficial.
The serum DHT level does not directly correlate with the production in peripheral tissues. DHT plays a critical function in the sexual development of males, beginning early in prenatal life. The role of DHT differs as males progress through the different stages of development; it has various impacts on their physiology during childhood, puberty, and even throughout adult life. As with any other disease, a deficiency or an excess of the DHT hormone leads to specific pathologies. These pathologies require identification and treatment for the adequate development and functioning of the genital organs, specifically in males.
Interventions aimed at reducing hair loss target both DHT production and DHT receptor binding within hair follicles. EGCG has also been shown to protect hair follicles — the part of your skin that grows hair — from hair loss caused by DHT. In particular, DHT plays an important role in the development of male external genitalia. It works in combination with testosterone to increase the size of the male external genitalia. It’s well known as a potentially beneficial treatment for an enlarged prostate and prostatitis due to its DHT-blocking ability. Because of this, it’s also thought to be a possible treatment for DHT-related hair loss, too.

No comments:
Post a Comment